2D Shapes and PerimeterUsing Attributes of 2D Shapes to Find Perimeter
In third grade, students are introduced to the idea of
Progression of finding the perimeter:
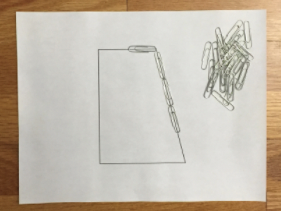
(1) Students use concrete object (like paperclips) to build the boundary
(2) Students find the distance around the shape by counting the

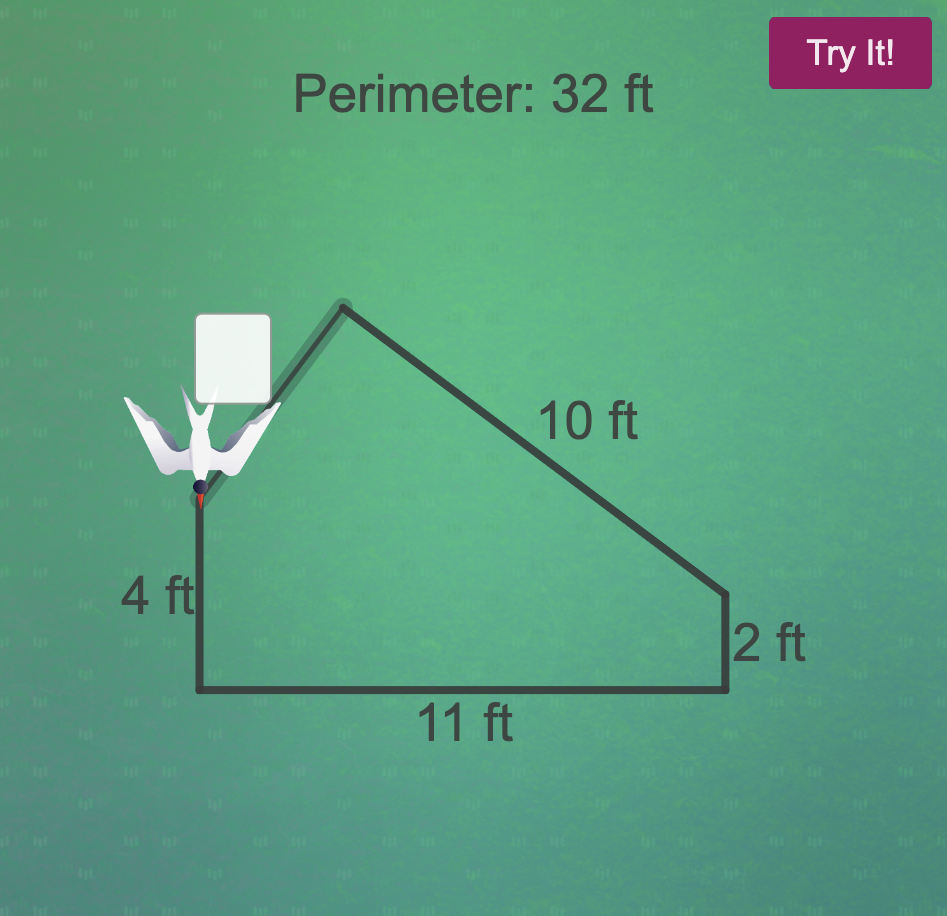
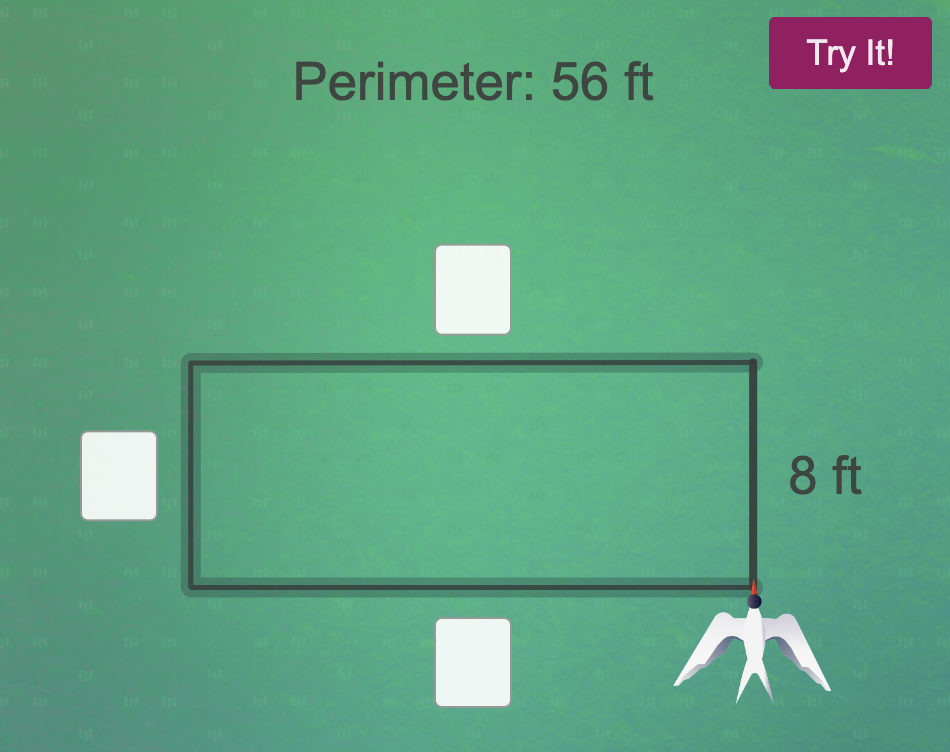
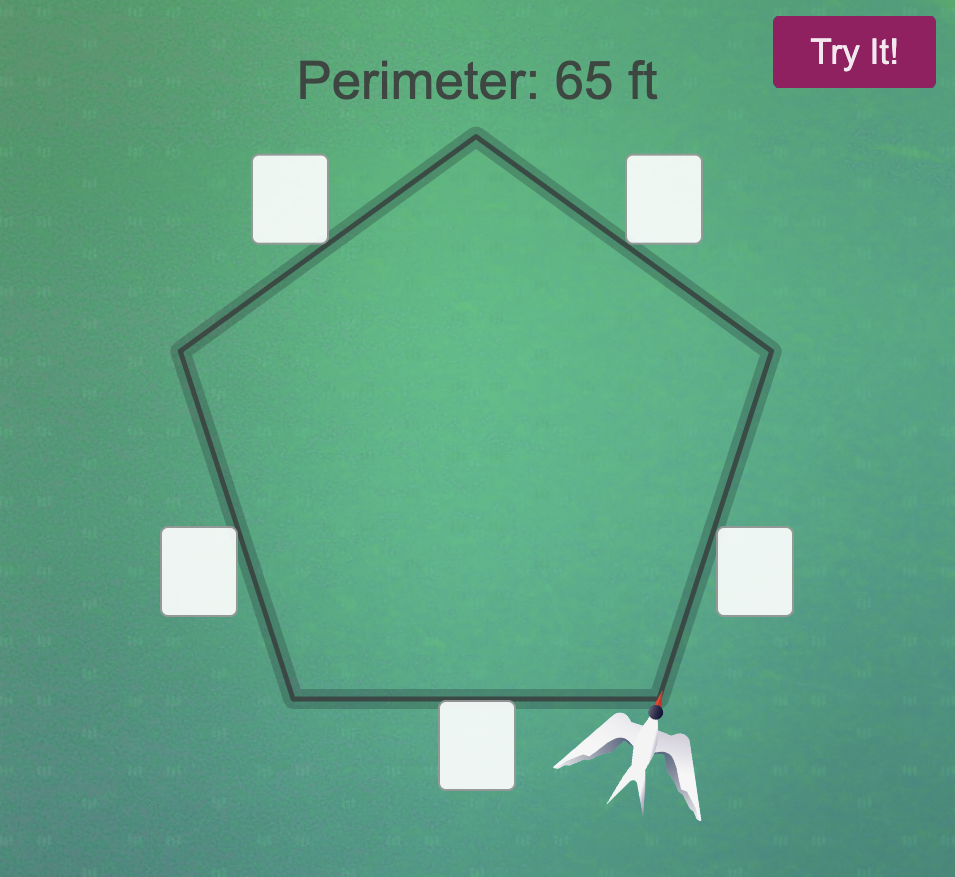
(3) Students use the geometric attributes of shapes to find perimeter more efficiently (by recognizing sides that are the same length and using multiplication).

Try these activities by entering some correct and incorrect values, to see what students will experience. Click on each of the images below to try it:
When finding perimeter, there are complexities in understanding linear measurements on grids. Consider the following problem. Who is correct?
Three students were asked to find the perimeter of this square:
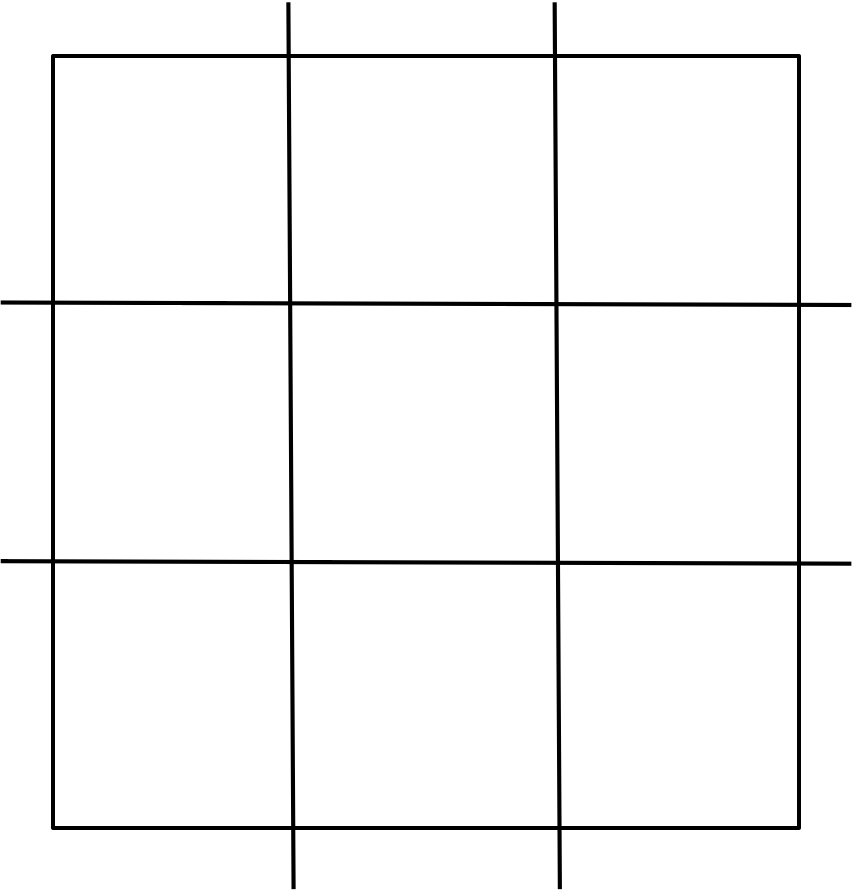
- Tyler: perimeter is 12 units
- Lexi: perimeter is 16 units
- Maggie: perimeter is 8 units
The correct student is